Tanzania’s National Bureau of Statistics (NBS) recently released the 2024 Integrated Labour Force Survey (ILFS), revealing a labour market in transition with significant gains in employment and literacy, but highlighting persistent challenges, including soaring informality, gender disparities, and youth unemployment.
The survey, conducted throughout 2024 across Mainland Tanzania and Zanzibar, offers the most robust, comparable, and harmonised labour market data the country has produced in recent years, marking a major milestone in Tanzania’s statistical capacity.
The survey employed a stratified two-stage sampling design based on the 2022 Population and Housing Census, covering 14,232 households (10,584 in Mainland Tanzania and 3,648 in Zanzibar).
Data were collected quarterly using Computer-Assisted Personal Interviewing (CAPI), achieving a 98.6% response rate and yielding information on over 61,500 individuals.
Table of Contents
Unemployment
National unemployment declined from 8.7% to 6.2%, though it remains higher among women (7.5%) than men (4.9%).
Youth unemployment (ages 15-24) stands at 10.0%, while Zanzibar experienced an increase from 7.7% to 10.9%.
The Labour Force Participation Rate increased from 72.1% in 2020/21 to 73.2% in 2024, while the Employment-to-Population Ratio rose from 65.8% to 68.7%, reflecting improved job absorption across the economy.
However, informality has grown from 92.5% in 2020/21 to 94.6% in 2024, with women slightly more affected than men.
The survey found that 74.8% of workers are classified as dependent contractors, while only 7.7% hold paid employment positions.
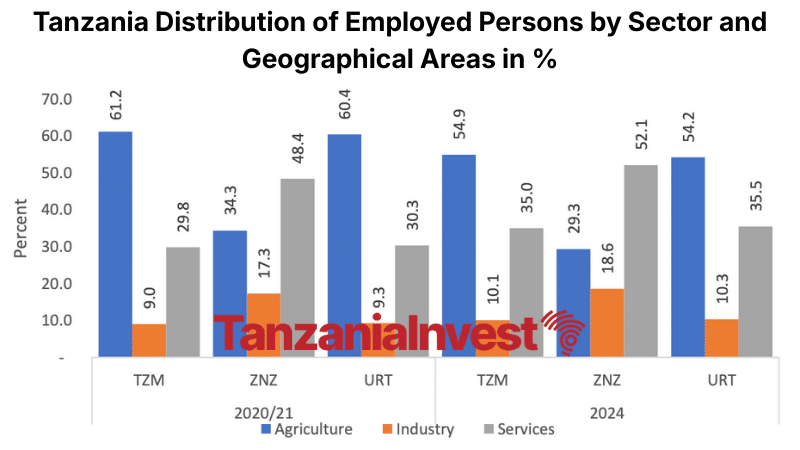
Agriculture remains the dominant employer but its share declined from 60.4% to 54.2%.
Employment in services increased to 35.5% and industry to 10.3%, indicating a gradual structural transformation of Tanzania’s economy.
Wages
Average monthly wages increased from TZS 393,861 to TZS 477,241.
However, significant gender wage gaps persist, with men consistently earning more than women across all education levels and geographical locations.
Urban workers, particularly in Dar es Salaam, earn substantially more than their rural counterparts.
Education and Literacy
Illiteracy fell dramatically from 17.8% to 11.5%, with particularly strong gains among young people aged 15-24, whose illiteracy rate dropped from 12.4% to 6.8%.
However, women and persons with disabilities continue to face higher illiteracy rates.
Policy Recommendations
The report recommends investing in skills development and retraining programs, particularly for women, youth, and persons with disabilities; reducing informality through enterprise formalization support; promoting gender equity through targeted training and equal pay measures; and diversifying employment by investing in high-potential sectors, including technology and the blue economy.
The findings are intended to inform policymakers as Tanzania pursues its Development Vision 2050, Zanzibar Development Vision 2050, and international commitments under the UN Sustainable Development Goals and African Union’s Agenda 2063.











