Beyond mortgage finance, significant opportunities for growth in housing microfinance exist in Tanzania, according to the Centre for Affordable Housing Finance in Africa (CAHF).
In its 2017 Housing Finance in Africa Yearbook CAHF indicates that the Tanzanian public sector, like other countries in the region, has been marginally successful at delivering affordable and sufficient housing for the urban poor.
Within this framework, the use of lower-cost technologies and materials is a key area of opportunity which complemented by the government’s initiatives to address housing gaps, has the potential to reduce costs associated with building and housing.
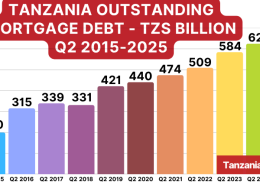
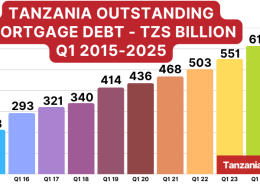
Tanzania has 58 commercial banks and other private financial institutions. However, interest rates are still relatively high, with an average Mortgage Interest Rate of 18% over a 25 years term.
Given affordability levels, the microfinance sector is especially important in addressing housing supply in Tanzania and is growing steadily, the yearbook reads.
It also highlights that a study commissioned by the Bank of Tanzania (BOT) found that 41% of Tanzanians who borrow microloans planned to use these for housing construction or improvements.
With more than 5,500 savings and credit cooperative societies and over 170 credit related Non-Government Organisations, there is an enormous potential for housing microfinance to contribute towards housing the majority of the population, the report concludes.
Tanzania Housing
Tanzania suffers from a shortage of good quality and affordable housing. The current housing deficit is estimated at three million housing units coupled with a 200,000 unit annual demand.