Measures to extend access to credit and reducing its cost are urgently required to support the economic growth of Tanzania, the World Bank (WB) indicates in its recent Economic Update on Tanzania titled “Money Within Reach – Extending Financial Inclusion in Tanzania”.
The report explains that limited access to credit represents a key constraint on the further development of the Tanzanian private sector, without which the country has only limited chances to achieve its industrialization objectives.
“International experience clearly shows that […] without affordable credit that supports investment in equipment, technology, and quality upgrade, Tanzanian firms cannot grow and be competitive on either regional or international markets,” the report reads.
Within this framework the role of banks in intermediating savings into credit remains underdeveloped compared to other regional peers and limited access to finance, as well as its high cost and short tenure remain amongst the critical issues which constrain the development of a vibrant private sector.
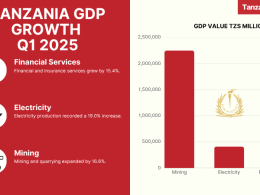
Interest rates remain very high and access to credit very restricted, as evidenced by the low ratio of credit to the private sector over GDP, which stands at less than 15%, compared to 36% in Kenya.
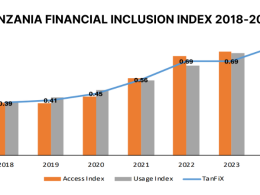
The Bank reminds that, at the same time, access to financial services in Tanzania has dramatically increased thanks to the adoption by the wider population of mobile money services.
The result is a bifurcated Tanzanian financial sector, with a very dynamic mobile financial services sector competing against a very concentrated banking sector.
To tackle this situation the WB suggests that the Government of Tanzania should make efforts to unlock competition in the banking sector, as well as ensuring a seamless integration between mobile and traditional financial services.
In particular, the Bank believes that measures should be taken to reduce the crowding out of public borrowing on the domestic credit market, which contributes to increased lending rates.
Also, improving the credit reporting system and the collateral recovery process, would help reducing the credit risk faced by financial institutions thus stimulating lending to businesses and SMEs.
Tanzania Financial Inclusion and Interest Rates
More than 60% of the Tanzanian population now has a financial account, compared to 11% in 2006, with most of these accounts being held with mobile money services.
However, the real cost of credit to the private sector is high, between 10% and 11%, with nominal interest rates at around 16%.