The Bank of Tanzania, through the National Council for Financial Inclusion (NCFI), has released the Annual Financial Inclusion Report 2024, showing major progress in the country’s financial inclusion.
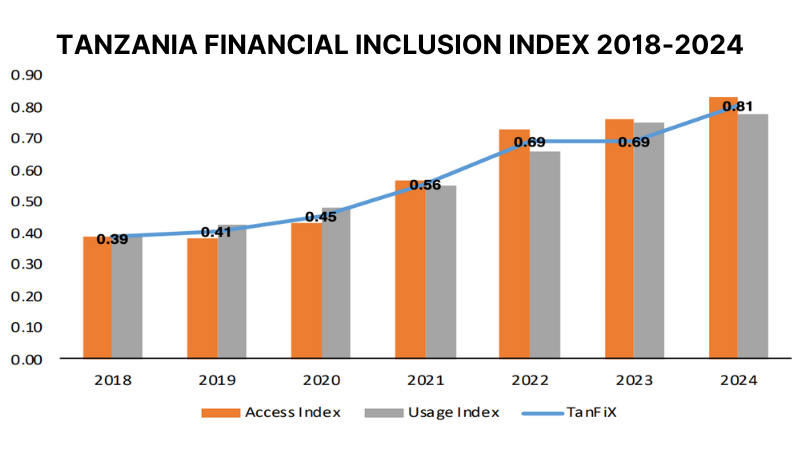
The Tanzania Financial Inclusion Index (TanFiX) rose from 0.69 in 2023 to 0.81 in 2024, reflecting the successful implementation of the third National Financial Inclusion Framework (NFIF 2023–2028).
The increase was largely driven by growth in financial access points and greater usage of financial services.
The access sub-index rose to 0.83, supported by mobile money and bank agents, microfinance Tier II, and community microfinance groups, while the usage sub-index increased to 0.78, boosted by microfinance and digital loans.
Financial Access Points and Digital Services Growth
The number of financial access points grew by 20.4% in 2024.
Mobile money agents increased by 18.97% to 1.48 million, while banking service access points rose by 36.6% to 146,505, with bank agents making up 99.3% of this growth.
Licensed microfinance access points grew by 21.4% to 62,312, and insurance access points increased by 42.5% to 2,208.
Digital financial services continued expanding. Active mobile money accounts grew by 17.5% to 60.75 million.
Digital loan accounts doubled to 193.33 million, with women owning 61.9% of them.
The total value of digital loans reached TZS 226.7 billion, with women borrowing TZS 152 billion (67%).
Digital insurance gross premiums reached TZS 1.4 trillion, supported by 17 independent digital insurance platforms and seven insurance companies adopting WhatsApp chatbots.
The Bank of Tanzania also endorsed the FinTech Regulatory Sandbox Regulations 2024 and launched its first cohort for testing innovative financial solutions. Progress was also made in research on Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
Financial Literacy and Consumer Protection
A total of 213 Certified Financial Educators were trained, reaching 31,902 beneficiaries through outreach programs. More than 27,000 individuals in rural areas received financial literacy training.
Financial literacy was integrated into school curricula, and mandatory financial education requirements for financial service providers were reinforced.
Market conduct supervision was intensified, and complaints handling mechanisms improved, with a 96.8% resolution rate for banking, credit, and payment services complaints.
Training and outreach programs mainly covered savings, investment, planning, and budgeting.
Policies, Programs, and Infrastructure
Local Government Authorities provided loans worth TZS 21.88 billion in 2023/24 to women, youth, and people with disabilities. Credit Guarantee Schemes supported micro, small, and medium enterprises’ access to finance.
The Warehouse Receipt System expanded from 190,000 farmer beneficiaries in 2023 to 2,429,711 in 2024, improving transparent pricing and timely payments for agricultural products.
The increase is due to increase in the number of agricultural produces included in the use of warehouse receipt system as well as the number of regions which formally were not using warehouse receipt system.
Infrastructure development supported financial inclusion, with over 21 million National IDs registered and 52.3% of hamlets electrified. The Tanzania Instant Payment System (TIPS) enhanced real-time interoperability for instant transfers.
Economic Impact and Outlook
According to the report, financial inclusion shows positive correlations with GDP growth, financial sector stability, and declining lending interest rates. It is also highlighted as a key driver for reducing poverty and unemployment.
Despite these gains, the report acknowledges challenges in deepening usage and improving service quality. The NCFI stated that it remains committed to sustained innovation, targeted policies, and strengthened partnerships to support Tanzania’s socio-economic transformation.