Avocados
Tanzania is the third-largest avocado producer in Africa, after South Africa and Kenya, and the 19th country in the world.
The latest figures by the Tanzania Trade Development Authority (TANTRADE) indicate that Tanzania produces an average of 190,000 tons of avocado fruits per year.
However, recent data from the Tanzania Horticultural Association (TAHA) indicates rapid expansion, with production increasing by an average of 20% annually over the past five years. Before 2020, annual production was below 50,000 tons, highlighting the significant recent growth trajectory.
Tanzania’s avocado exports increased from 17,711.49 tons, valued at USD 51 million in 2021/2022, to 26,826.30 tons, valued at USD 77.3 million in 2022/2023.
Projections for the 2023/2024 season estimate exports reaching 31,950 tons.
Tanzania’s avocados are exported primarily to Europe (accounting for 40% of exports), India (30%), the Middle East (19%), and other markets, including South Africa and Kenya (combined 11%). Key European destinations include Denmark, France, the Netherlands, Norway, Spain, and the UK.
Tanzania Avocado Production
Avocado is a relatively new crop that Tanzania started exporting in 2009.
As avocados thrive in subtropical climates and areas suitable for coffee and tea (Tanzania’s traditional crops), Tanzania is an ideal location for avocado growth.
Tanzania’s total avocado production is difficult to estimate due to a lack of comprehensive data from Tanzania’s responsible ministry or institutions. Consequently, there is data inconsistency among different sources.
The latest figures by the Tanzania Trade Development Authority (TANTRADE) indicate that Tanzania produces an average of 190,000 tons of avocado fruits per year.
However, recent trends show production has been increasing by an average of 20% annually over the last five years. Before 2020, annual production was below 50,000 tons.
Commercial production/export of avocados is dominated by Rungwe Avocado Company Ltd and Africado Ltd, which is based in Siha District, Kilimanjaro region. Major investments have also been made by companies such as Kibidula, AvoAfrica, Kakuzi, and Avodemia.
The rest of the growers are smallholder farmers who own a couple to hundreds of avocado trees around their homesteads and in distant farms.
The popular avocado varieties produced in Tanzania are Hass, Fuerte, Pinkerton, and, to some extent, Puebla.
Tanzania’s prominent avocado-producing areas are in the regions of Mbeya, Njombe, Songwe, and Iringa in the southwest, as well as in Kilimanjaro, Arusha, and Tanga in the northeast of the country, where coffee and tea are traditionally grown.
The other regions are Kigoma and Kagera in the northwest and Morogoro in the east of Tanzania.
Tanzania Avocado Exports
According to TAHA, Tanzania’s avocado exports increased from 17,711.49 tons, valued at USD 51 million in 2021/2022, to 26,826.30 tons, valued at USD 77.3 million in 2022/2023.
Exports for the 2023/2024 season are estimated to reach 31,950 tons.
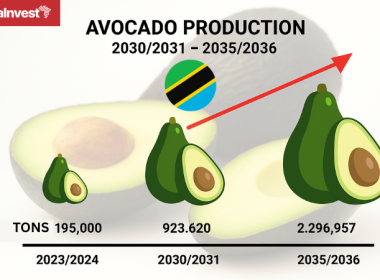
Long-term projections suggest production could reach 923,620 tons by 2030/31 and 2.29 million tons by 2035/36, with potential export revenues climbing to USD 714 million and USD 2.8 billion, respectively, in those years.
The top destinations for avocados from Tanzania are Europe (40%), India (30%), where they are exported duty-free, and the Middle East (19%). Key European markets include France and the Netherlands. The United Kingdom is also a significant importer.
Other markets with large untapped export potential include Japan, Switzerland, Spain, Germany, the United Arab Emirates, and China, while the potential to export avocado to other African countries is smaller, though South Africa presents a seasonal window (October-January).
In August 2021, Tanzania’s Prime Minister Kassim Majaliwa announced that the government was finalizing negotiations with South Africa to export avocados to the latter.
And Tanzanian Deputy Minister for Agriculture, Hussein Bashe, said that the government was working to open other avocado markets including China and India.
Eventually, in November 2021, the National Plant Protection (NPPZA) – Department of Agriculture of South Africa granted market access to the importation of avocados from Tanzania.
In addition, from 25th November 2021, the Indian Plant Health Authority allowed for the first time to export avocados from Tanzania to India. In March 2022, the Minister of Agriculture of Tanzania disclosed that these exports would be duty-free in India, providing a significant advantage over competitors like Kenya who face a 30% duty.
To seize the opportunity represented by the increasing international demand for avocados, Tanzania established an avocado cluster in the northern zone regions in May 2021.
Furthermore, in November 2022, Tanzania and China signed 15 bilateral cooperation documents that include a protocol of Phytosanitary Requirements for the Export of Fresh Avocado Fruits from Tanzania to China. However, market access involves a lengthy registration and certification process, and offered prices tend to be lower than in other markets.
The Ministry of Agriculture confirmed that China would start inspecting avocado farms in March 2024 before giving local exporters the green light to export the fruits to the Asian country.
Tanzania’s Ministry of Agriculture also announced plans to establish a shared facility in the southern highlands to collect, sort, grade, and pack all the region’s avocados to ensure consistency of product quality before shipment.
The government also intends to establish a “green channel” to facilitate the export of quality fresh produce from farm to market.
Investment Opportunities in the Avocado Sub-sector in Tanzania
The Tanzania Investment Centre (TIC) published a report titled “Investment Opportunities in the Avocado Value Chain, Tanzania,” in which it highlights the following opportunities:
–Opening large plantations to produce larger volumes of fruits for export (to capture Asian, European, and American markets), without excluding other African countries that do not produce avocados. Such plantations can be in the Southern Highlands of Tanzania (Mbeya, Iringa, Njombe, Ruvuma, Rukwa, and Katavi), Northern Zone (Arusha, Kilimanjaro, and Tanga), Lake zone (Kagera and Mara,) and Morogoro regions.
–Investing in facilities that process avocados: sorting, cleaning, grading, packaging, production of assorted salads (foodstuffs), cooking oil, cosmetics, soap products, etc. This includes investment in modern technology like optical sorting machines.
-Manufacture or supply of inputs required in the entire avocado value chain – seeds, pesticides, fungicides, fertilizers, farming equipment/implements (tractors, trailers, harvesting machines), processing & packaging machinery, avocado packaging materials (specialized boxes for transporting avocados), cold rooms, etc. Now, all packaging materials are sourced from Kenya.
Last Updated: 17th April 2025
Sources: International Trade Centre (ITC), Research on Poverty Alleviation (REPOA), Southern Agricultural Growth Corridor of Tanzania (SAGCOT), Tanzania Horticultural Association (TAHA), Tanzania Investment Centre (TIC), Tanzania Private Sector Foundation (TPSF), Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.